Stay informed of free updates
Just register at American inflation Myft Digest – Delivered directly in your reception box.
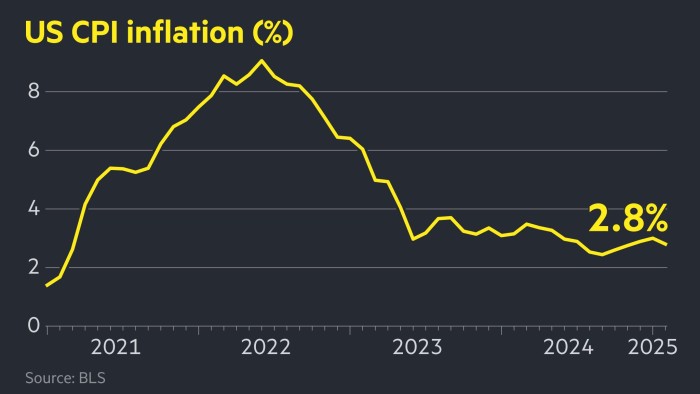
American inflation has dropped more than expected at 2.8% in February, strengthening the case so that the Federal Reserve reduces interest rates in the midst of signs of slowing growth in the greatest economy in the world.
The annual figure of the consumer price index on Wednesday was less than 3% of January and the 2.9% expected by economists, according to a reuters survey.
American actions opened higher, but the gains collapsed later in the negotiation session, leaving the S&P 500 from Blue Chip S&P 500 during the day.
The term markets are prices in two rate drops this year with around 85% of a third – up slightly before the release of the data.
The American central bank faces a difficult balancing act as it tries to lower inflation without triggering a recession, in the midst of intensifying fears that the aggressive economic agenda of President Donald Trump obstructs growth.
Companies and financial markets were shaken by the chaotic deployment of Trump prices on the largest trade partners in the United States, which was marked by a series of sudden climbing and turn-turn.
Wednesday figures showed that central inflation increased by 3.1%, going down expectations of an increase of 3.2%.
“The underlying inflation slows down before reaching these risks upwards, which will come later in the spring, so it’s positive for the Fed,” said Veronica Clark, economist of Citigroup. “It will make them less worried about planning the cuts later in the year.”
Last week, the president of the Fed, Jay Powell, expressed his concerns concerning the health of the American economy after the post-electoral gains of the S&P 500 index were destroyed after the publication of disappointing figures for February.
Powell suggested that he expected the central bank to have interest rates at their current range between 4.25% and 4.5% at his meeting next week, claiming that the Fed was not “pressed” to cut and “focused on the separation of the noise signal as the prospects are evolving”.
On Wednesday, the Bank of Canada reduced interest rates by a quarter to 2.75%, citing the expected slowdown in “trade tensions and increased prices imposed by the United States”.
Although he said that the Canadian economy had started the year in good shape, the BOC also noted the slowdown in economic activity in the United States and warned that its own perspectives were more difficult to understand due to “uncertainty more than usual because of the rapidly evolving political landscape”.
Some economists and investors fear that Trump prices will implate American inflation, with the price of several metals, including aluminum, increasing after the administration has imposed high prices on Wednesday imports.
The move of the White House to impose 25% samples on all imports of steel and aluminum has triggered rapid reprisals of the EU, which targets up to 26 billion euros in American goods with prices.
Tom Porcelli, US chief economist at PGIM FIXED RENCE, said the decrease in February was welcome, but said that investors’ alleviation could be short -term given the possible prices.
In February, the sectors recorded the most important price increases included medical care and used cars, while aerial declines and new cars were among those where costs have decreased.
Egg prices, an important contributor to solid read of January, was again higher in February, increasing by 10% over the month for an annual increase of 59%.
“This is good news, that’s for sure, but I think we don’t want to overestimate this,” said Ryan Sweet, chief economist in the United States at Oxford Economics. “Only the prices on China had entered into force in February and it can be a little too early to be captured in this series of data.”